Page 17 - Southlake FY23 Budget
P. 17
TRAnSmITTAL LETTER
LONG-TERM DEBT DEBT AS % OF ASSESSED VALUATION
3.50% $120,000,000
3.01% Desired Range
3.00% 2.79% $100,000,000
2.36%
2.50%
2.07% 2.00% $80,000,000
VALUATION 2.00% 1.71% 1.51% $60,000,000 DOLLARS
OF 1.50% 1.46% 1.49% 1.49% 1.37% 1.19%
PERCENTAGE 1.12% 0.92% $40,000,000
0.72% 0.58%
1.00%
0.50% 0.44% 0.34% 0.27% 0.22% 0.24% $20,000,000
0.00% $-
2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023
FISCAL YEAR
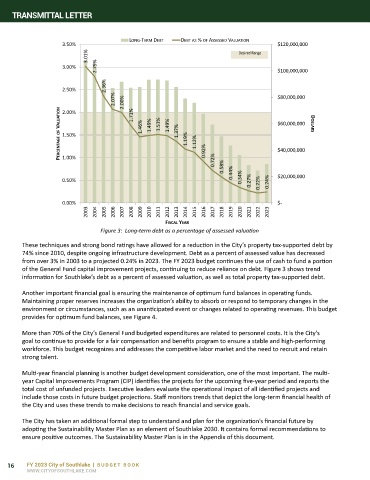
Figure 3: Long-term debt as a percentage of assessed valuation
These techniques and strong bond ratings have allowed for a reduction in the City’s property tax-supported debt by
74% since 2010, despite ongoing infrastructure development. Debt as a percent of assessed value has decreased
from over 3% in 2003 to a projected 0.24% in 2023. The FY 2023 budget continues the use of cash to fund a portion
of the General Fund capital improvement projects, continuing to reduce reliance on debt. Figure 3 shows trend
information for Southlake’s debt as a percent of assessed valuation, as well as total property tax-supported debt.
Another important financial goal is ensuring the maintenance of optimum fund balances in operating funds.
Maintaining proper reserves increases the organization’s ability to absorb or respond to temporary changes in the
environment or circumstances, such as an unanticipated event or changes related to operating revenues. This budget
provides for optimum fund balances, see Figure 4.
More than 70% of the City’s General Fund budgeted expenditures are related to personnel costs. It is the City’s
goal to continue to provide for a fair compensation and benefits program to ensure a stable and high-performing
workforce. This budget recognizes and addresses the competitive labor market and the need to recruit and retain
strong talent.
Multi-year financial planning is another budget development consideration, one of the most important. The multi-
year Capital Improvements Program (CIP) identifies the projects for the upcoming five-year period and reports the
total cost of unfunded projects. Executive leaders evaluate the operational impact of all identified projects and
include those costs in future budget projections. Staff monitors trends that depict the long-term financial health of
the City and uses these trends to make decisions to reach financial and service goals.
The City has taken an additional formal step to understand and plan for the organization’s financial future by
adopting the Sustainability Master Plan as an element of Southlake 2030. It contains formal recommendations to
ensure positive outcomes. The Sustainability Master Plan is in the Appendix of this document.
16 FY 2023 City of Southlake | BUDGET BOOK
WWW.CITYOFSOUTHLAKE.COM