Page 171 - CityofSouthlakeFY26AdoptedBudget
P. 171
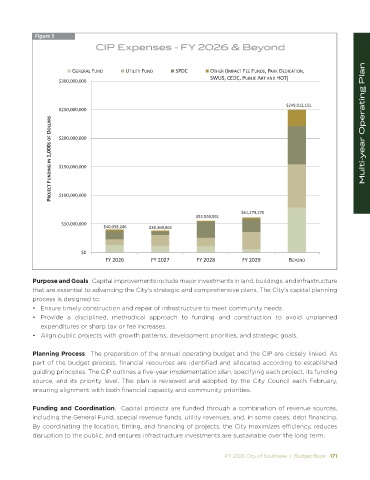
Figure 5
CIP Expenses - FY 2026 & Beyond
' E Z > &hE hd/>/dz &hE ^W Kd, Z ;/DW d & &hE ^͕ W Z< / d/KE͕
^th^͕ ͕ Wh >/ Zd E ,KdͿ
ΨϯϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ
ΨϮϰϵ͕ϵϭϮ͕ϭϱϭ
ΨϮϱϬ͕ϬϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ
K>> Z^ Multi-year Operating Plan
K& ΨϮϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ
ϭ͕ϬϬϬ^
/E ΨϭϱϬ͕ϬϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ
&hE /E'
WZK: d ΨϭϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ
Ψϲϭ͕Ϯϳϵ͕ϮϳϬ
Ψϱϱ͕ϱϱϬ͕ϱϵϭ
ΨϱϬ͕ϬϬϬ͕ϬϬϬ
ΨϰϬ͕Ϭϱϴ͕Ϯϰϲ Ψϯϴ͕ϯϲϬ͕ϴϲϯ
ΨϬ
&z ϮϬϮϲ &z ϮϬϮϳ &z ϮϬϮϴ &z ϮϬϮϵ zKE
Purpose and Goals. Capital improvements include major investments in land, buildings, and infrastructure
that are essential to advancing the City’s strategic and comprehensive plans. The City’s capital planning
process is designed to:
• Ensure timely construction and repair of infrastructure to meet community needs.
• Provide a disciplined, methodical approach to funding and construction to avoid unplanned
expenditures or sharp tax or fee increases.
• Align public projects with growth patterns, development priorities, and strategic goals.
Planning Process. The preparation of the annual operating budget and the CIP are closely linked. As
part of the budget process, financial resources are identified and allocated according to established
guiding principles. The CIP outlines a five-year implementation plan, specifying each project, its funding
source, and its priority level. This plan is reviewed and adopted by the City Council each February,
ensuring alignment with both financial capacity and community priorities.
Funding and Coordination. Capital projects are funded through a combination of revenue sources,
including the General Fund, special revenue funds, utility revenues, and, in some cases, debt financing.
By coordinating the location, timing, and financing of projects, the City maximizes efficiency, reduces
disruption to the public, and ensures infrastructure investments are sustainable over the long term.
FY 2026 City of Southlake | Budget Book 171